In this video, we’re going to look at how our brand impacts the SEO results of non-branded queries.
Video Transcript:
Branded Vs. Non-Branded Queries
What’s the difference between branded queries and non-branded queries? In case you don’t know, a branded query is a query that includes your website’s brand name, or maybe a variation of your brand name, something that’s unique to your domain. A non-branded inquiry is pretty much everything else.
Keywords that don’t reference a brand name or any part of it, including misspellings. That’s the difference between these two, branded have to do with your brand, and non-branded has to do with everything else. More likely what your brand does. Those are those keywords that you’re writing blogs about, things that you’re trying to earn traffic on.
The Truth about Branded Queries
The truth about branded queries is that a lot of businesses ignore them. They assume that because it’s their brand name, they’re going to naturally rank for them and that it’s all going to be good.
This is dangerous in today’s Google for a number of reasons. And these are just a few, not all of them. The first one is your domain might not be ranking for your branded queries. Google might not know much about your brand. Maybe it’s not able to crawl or index your site. Maybe your brand is too closely related to another term. That term’s ranking for it.
There are a lot of reasons why your brand may not be ranking for its own name. You also could have incorrect listings. Maybe you have the wrong pages showing up. Maybe you have the wrong profiles. Maybe your Facebook’s showing up, but your website’s showing up below it. Maybe it’s out of whack on the brand results. Maybe you have bad reviews from other websites that are ranking ahead of your brand name.
This happens quite a bit when brands ignore their brand. And then it turns out that they have all these bad reviews ranking for branded queries. And then the last, maybe you have missing information. Maybe there’s incorrect information showing up in the knowledge panel or in a local pack or in a listing somewhere. And if you’re not being aware of that, you have some inconsistencies within your brand on Google, and that can impact how Google sees and views your brand and the quality of your brand.
Entities, Your Brand and Non-Branded Queries
On this channel, we’ve talked a lot about structured data. We’ve talked a lot about entities and how Google has made this shift from strings, so text, to things, which are entities. These are things or concepts that are singular, unique, they’re well defined, and distinguishable. A lot of times we think of entities as those keywords that we’re targeting.
For instance, in our business, we target terms like SEO. SEO is an entity. It’s a concept that’s singular, but in the same regard, so is our brand. SMA Marketing is an entity. It’s a thing. It’s a concept, it’s singular, it’s unique. It’s well defined and it’s distinguishable. And those keywords that we’re targeting are also connected and related to our brand. They’re related to our brand’s entity and how Google understands it because those keywords describe our brand.
Those keywords and our brand are closely related when we look at the world of linked open data and knowledge graphs, as Google is, and how those things start to work in play together. If we’d zoom in on certain brand entities, we would notice different attributes associated with them. If we did some sort of TensorFlow visualization on some of these entity audits or extractions that we do.
In the same regard, you have to think of your brand as an entity itself and those keywords, those non-branded terms, as things that define it. And if we look at the organizational markup within schema.org, you’ll notice there are a lot of ways that non-branded queries can show up in this process.
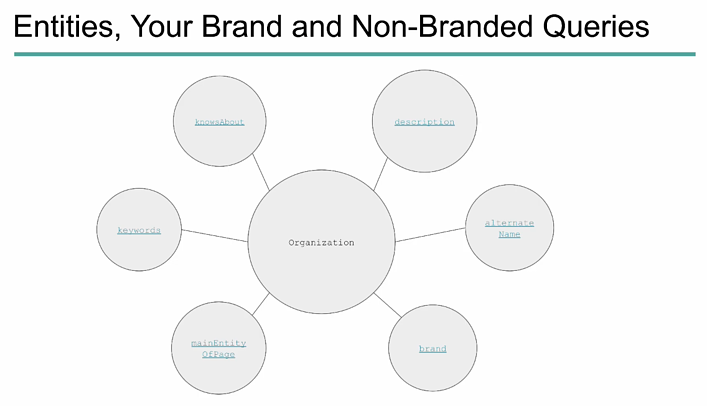
In the center here, we have ‘organization’. There are a ton of different attributes that we can add to an organization when we’re marking it up and helping Google understand our entity better. But one of those things is ‘keywords’ where you can put in specific terms that are related directly to your organization, but you can also write up what your brand ‘knows about’. These are those different concepts that your brand is maybe authoritative on. You have a ‘description’, oftentimes which includes those non-branded keywords.
You have ‘alternate names’ for your brand. This may help if your brand has one name, but goes by something else. For instance, when I first started this agency, we were Shelley Media Arts, and then we rebranded and shifted under SMA Marketing. We add both of those names into our organizational markup because it’s an alternate name that could be used for our brand itself.
You also have something called ‘brand’ that you can tag as well as the main entity of the page. On a specific page, what is this main entity? What is this specific page about? And even though it’s about maybe SEO, that’s still connected to your organization as a whole. As you can see right here in a visual way, our organization, and our brand is much connected to those non-branded queries.
E-A-T and Your Brand
How does this impact the search results? Well, Google’s talked a lot in the past about E-A-T. We’ve seen it in the quality guidelines, there are a lot of people in the SEO world that talk about E-A-T and it stands for expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
And this is looking at the creator of the main content, the main content itself and the website. If you look at your main content and who’s the creator, oftentimes it’s the organization that’s being attributed with that content. Google’s looking at this content and saying, are you an expert? Do you have authority? Are you trustworthy?
Google will tell you that E-A-T is not a rank factor directly, but I believe it has a major impact on ranking and does a whole lot of people in the world of search. I think we can see this with the way search has moved, that sites that don’t have the expertise, that aren’t authoritative, that aren’t trustworthy begin to slide in the results.
I’ve seen brands where they’ve not taken care of their brand results, and lose out on some queries that they used to rank for because their brand got diluted. Their brand became less of an expert. The brand became less authoritative and trustworthy. And as a result, they lost lots of site traffic, not only from branded queries but also began to impact non-branded queries, as well as Google, saw them as less of a brand of trust.
If you want your brand to be known for a query, you have to be an expert. You have to prove that you’re an expert. You have to have authority, and you have to show that you can be trusted. And if your brand’s lacking in these areas, you’re going to have a hard time ranking for anything, not just branded terms, but non-branded terms as well.
How to Improve Your Brand for SEO
1. Track and Review Your Brand Queries
What can you do? How can you help improve your brand SEO? Well, the first thing you need to start doing is tracking and reviewing your brand queries, looking at the things you’re ranking for. For instance, if you have your brand reviews, do your websites show up, do your links show up, and are they positive? Are they negative? And if they’re negative, what are you going to do to help jump that?
This is an instance that we’ve faced a number of times with companies as we start working with them, we say, ‘Hey, you have some of these branded queries that aren’t good, and we need to try to work on helping improve your brand and the visibility of your brand.’
2. Track Brand Mentions
You also want to track your brand mentions. How often are people mentioning your brand? And if they are, is it in a positive light or not? And again, what action can you take?
3. Get Brand Listed on Reputable Sites
You also want to make sure that you’re listed on reputable sites. This isn’t about blindly putting links on websites, but if there are sites within your industry that make sense for you to be on and they’re reputable and they can help show that you are trustworthy, those are good.
And not just from a backlink standpoint. So if Google sees, okay, this is an organization that promotes a certain part of your industry and all of the competitors are on there and it’s known as a well-known organization and group, you should probably be on there too. And looking for those opportunities to improve your brand and its reputability by being on those sites.
4. Give Attribution When Making Claims
You also need to make sure you’re making attribution or giving attribution when you’re making claims. If you’re writing pieces of content and you’re showing your expertise, or you’re showing that you know what you’re talking about, linking and quoting other experts is helpful in that because you’re saying, ‘Hey, I believe this, and so does all these other people that Google’, you already think as being reputable.
That helps with your users because they know that you’re not pulling stuff out of midair, but it also helps Google say, okay, this guy, isn’t making his claim on his own. It’s backed by a number of people in this space as well.
5. Optimize Knowledge Panel/Local Listing
You also want to be optimizing your knowledge panel, if you have one, optimizing your local listing, make sure that the information is correct. Make sure that your information is correct on your website as well. And any of those other platforms where your business information may be showing up and making sure that it’s congruent and consistent, that’s important. And as you begin to do this, you can build the reputability of your brand. You can build the strength of your brand, the expertise, the authoritativeness, and the trustworthiness.
There’s a whole lot more that you can do in the world of brand SERPs. And I’m going to make a quick pitch here for this book that I highly recommend for you to check out. I’m not getting anything for posting this on here, but Jason’s book is good and it will help you especially if you’re new to the world of brand SERPs or brand SEO.
I like this book. I use this book all the time. I think it’s a great resource. So go ahead and check this out if you have some time, you can listen to it, read it, do whatever you need to do, but start to take ownership of your brand. That way you can get the results you want from the non-branded queries as well. Until next time, happy marketing.



